What is a Line Tester and How Does It Work?
A line tester is an essential tool in electrical work. It helps ensure that electrical circuits are functioning properly. This device can identify issues such as breaks or faults in lines. For both professionals and DIY enthusiasts, understanding how a line tester works is crucial.
Using a line tester can seem straightforward, yet it requires care. The test should be conducted with the right mindset. Users must pay attention to the details. A simple oversight could lead to dangerous consequences. The device has a light indicator, which shows whether the circuit is live or dead.
While line testers are effective, they are not foolproof. Users need to double-check their findings. Mistakes can occur if the device is not used correctly. In this article, we will explore the components of a line tester and how to operate it safely and effectively. Understanding its function can prevent accidents and improve outcomes in electrical projects.
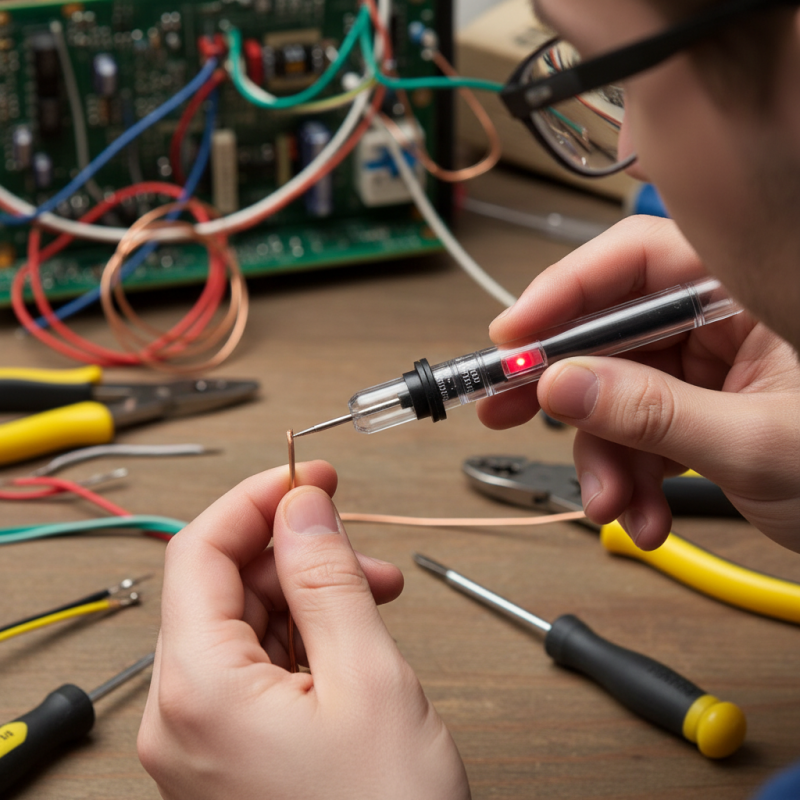
What is a Line Tester?
A line tester is a crucial tool for electricians, ensuring
safety and efficiency during electrical work.
These devices check the integrity of electrical lines. They can identify issues such as breaks or shorts in circuits.
According to industry reports, about 25% of electrical faults are due to
improper line testing. This highlights the importance of using the right tools.
Line testers come in different forms. Some are simple pen testers that provide basic functionality. Others are more advanced
and can give detailed readings. Recent data shows that using more sophisticated testers can reduce troubleshooting time
by up to 30%. However, many professionals still underestimate
the importance of regular testing. The oversight can lead to prolonged downtime
and increased costs.
Moreover, some line testers display results differently. Users need to be trained to understand these readings fully.
Misinterpretation of data can happen. This isn't uncommon, especially among less experienced electricians.
Adequate training can bridge this gap. Investing time in learning
can eliminate mistakes. Ultimately, understanding what a line tester does is vital for
optimal electrical work.
Key Components of a Line Tester
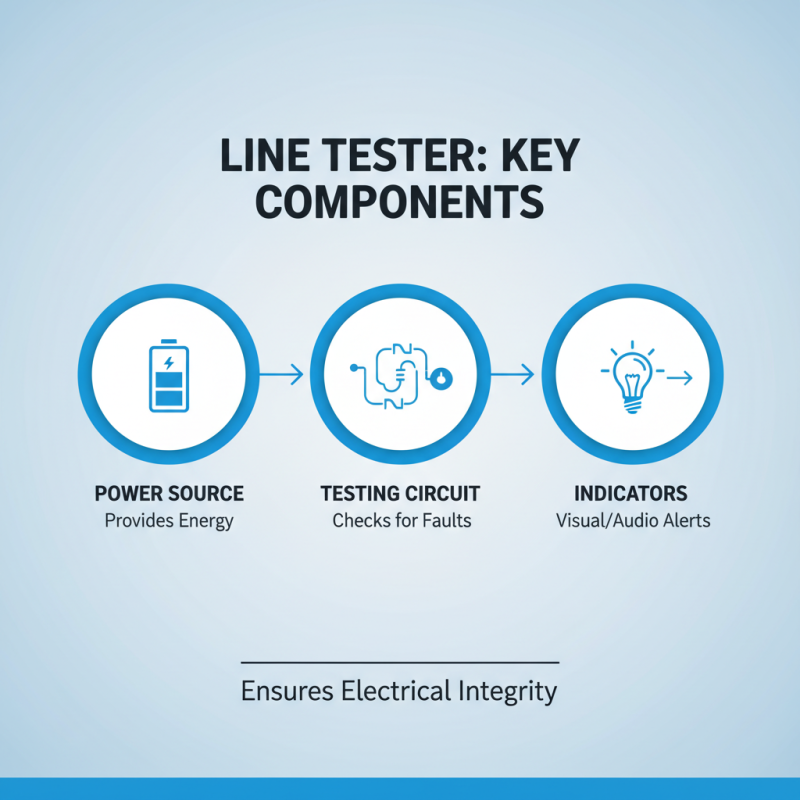
A line tester is a vital tool used to check the integrity of electrical connections and circuits. Understanding the key components of a line tester can help technicians and electricians use this tool effectively. At its core, a line tester comprises a power source, a testing circuit, and indicators for results. Each component plays an essential role in detecting faults.
The power source provides the necessary voltage for the test. It can be powered by batteries or directly from the circuit being tested. The testing circuit connects to the line under investigation. It may include various resistors and capacitors, allowing for different test scenarios. The indicators, often comprising lights or meters, reveal whether the line is live or faulty. This feedback is crucial for ensuring safety and effectiveness.
Using a line tester is straightforward but can be tricky. Users must ensure that the device is calibrated correctly. If not, false readings can lead to mistakes. A simple test might yield inaccurate results if the equipment is not functioning well. Always double-check connections before proceeding with tests. This attention to detail is vital for safety and accuracy.
How Line Testers Function: The Mechanism

Line testers are essential tools in various industries, especially telecommunications and electrical sectors. They help verify the integrity of lines and connections. A line tester operates on simple principles of electrical conductivity. It measures the voltage, current, and resistance in circuits. This helps technicians identify faults or weakness in lines.
A typical line tester consists of probes for connection and a display for readings. The data can provide information about short circuits or open lines. According to industry reports, around 30% of service disruptions are linked to faulty lines. Technicians use line testers to reduce downtime. They can accurately pinpoint issues within minutes, which is more efficient than manual checking.
However, line testers aren't foolproof. Some issues may not show up until conditions change. For example, temperature fluctuations can affect readings. Additionally, they require proper calibration to ensure accurate readings. A poorly maintained tester may lead to false results. It's crucial for technicians to regularly check their line testers for reliability.
Applications of Line Testers in Various Industries
Line testers are crucial in various industries. They assess the integrity of electrical lines and detect faults. In the telecommunications sector, the demand for reliable connectivity drives the utilization of line testers. According to industry reports, about 70% of downtime results from line issues. The use of line testers minimizes this downtime significantly.
In construction and maintenance, line testers ensure safety and functionality. Electricians often use these tools when working on power lines. A recent study highlighted that proper testing before installation reduces safety incidents by 40%. However, not all technicians fully understand the features of these testers. This gap can lead to inefficiencies and overlooked problems.
In transportation, line testers play a key role in maintaining rail systems. They help in checking signal lines for faults. Research indicates that regular testing can enhance operational efficiency by up to 30%. Still, some organizations neglect routine checks, risking safety and delays. Adopting regular line testing can lead to a more reliable transport infrastructure.
Applications of Line Testers Across Industries
Maintenance and Safety Considerations for Line Testers
Line testers are essential tools in electrical maintenance. They help ensure safe operations by identifying faults in power lines. However, using these devices requires careful attention to safety standards. Safety goggles and gloves should always be worn to protect against accidental shocks. It's easy to overlook these precautions, especially in familiar environments.
Regular maintenance of line testers is critical. Inspect the device after each use. Look for signs of wear and damage. A small crack can lead to significant hazards. Users should also ensure the tester is calibrated correctly. This can prevent incorrect readings that may cause misjudgments in repairs.
Training is paramount. Many users underestimate the importance of adequate knowledge. Understanding the device's limitations can prevent accidents. It's vital to stay updated on safety protocols. Knowledge gaps can be dangerous. Each user should reflect on their readiness. Are there areas for improvement? Awareness can make all the difference in maintaining safety while using line testers.
What is a Line Tester and How Does It Work? - Maintenance and Safety Considerations for Line Testers
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Type of Line Tester | Digital, Analog, or Multimeter |
| Measurement Accuracy | ±0.5% of reading |
| Input Voltage Range | 0-600V AC/DC |
| Safety Rating | CAT IV 600V |
| Battery Life | Up to 200 hours |
| Temperature Operating Range | -10°C to 50°C |
| Calibration Frequency | Every 12 months |
| Common Applications | Electrical maintenance, troubleshooting circuits, testing outlets |
| Common Safety Considerations | Use personal protective equipment, ensure device is rated for application voltage |
Related Posts
-

Innovative Solutions for Precision Line Testers
-

How to Choose the Best Phone Testing Equipment for Accurate Results
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Phone Testing Equipment for Your Needs
-
Top Quality Testing Equipment for Accurate Results?
-

Maximizing Efficiency with Field Test Equipment Advantages for Your Business
-

What is Pile Testing Equipment and How Does it Ensure Structural Integrity





